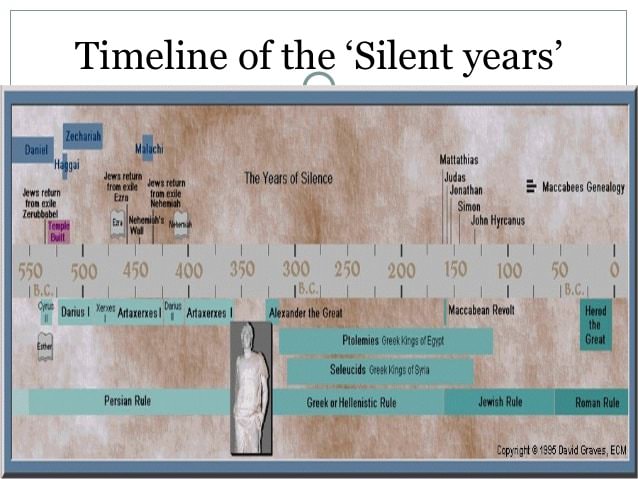
If you turn in your Bible from the last page of Malachi you are immediately in Matthew 1. Historically there is about 400 years in that page turn. It is called the 400 ‘silent years’ by scholars because although God was working there were no prophets speaking, and no Scripture being written to Israel until John the Baptist arrives in the desert.
A brief overview of the history we have covered so far will help to orientate you with these 400 years.
Galatians 4:4 says, “But when the time had fully come, God sent his son, born of a woman, born under the law, to redeem those under law, that we might receive the full rights of sons.” In this period God was preparing the world for the perfect situation for Jesus to come to earth. He was ‘silent’ but working none the less.
Dr. Bert Downs breaks up this history into three parts: rulers, readings and religions.
Rulers
We leave the Old Testament with Israel under the power of the Persian Empire. Their rule continues to 331 B.C. The Persians are key in history because if you remember their foreign policy allowed for the return of the exiles to Jerusalem. They allowed for the population of Jerusalem, the building of the Temple, and securing of the city. But the rule of Persia doesn’t last and in 331 B.C. Alexander the Great conquers the Persians and sets up Greek rule until about 164 B.C. Greek rule came with profound influence to God’s people. Greek culture pervades the land. This culture is an educated, multi-god worshiping culture full of magic and special ceremonies. Perhaps the most important impact they had, outside of culture, was that they brought a language. They brought the Greek language that would become the language of the land. Most people become bilingual. Greek will stay in place as the language, even as Greece loses control of this area, which it ultimately does.
The Greeks eventually loose their ability to control and a group lead by a priest overthrow Greek rule and the people of Judah effectively rule themselves from 154 B.C to about 63 B.C. It is referred to as the Hasmonean dynasty – starting with the Maccabean revolt against Greek rule. Much of the history is recorded in the books Maccabees in the Apocrypha. The time under ‘their own rule’ is one of battle for land and religion.
The Hasmonean dynasty ends in about 63 B.C when General Pompeus makes Judah a client of Rome. The Romans rule until 135 A.D. The Romans bring law, judicial systems, peace, stable government and systems. Notably the Romans are furious road builders. They connect almost their whole empire: Roads that will carry the message of the Gospel far and wide.
Readings
Four major works come out of this period. Firstly, the Apocrypha. The Apocrypha was a group of books, about fifteen of them, never credited as Scripture but worth reading for good history. Also when you read them you will realise the difference between them and inspired, authoritative Scripture –it is quite obvious. If you have a Bible that is used in the Roman Catholic Church, or typically in the Orthodox Church, you will find these books in the middle of that Bible edition.
Secondly, the Pseudepigrapha. The pseudepigrapha were basically sectarian writings. They tended to focus on values and thoughts of people of the time. There were sixty or so, various kinds of writings that also make up an important group of historical things that we want to keep track of.
Thirdly, the Dead Sea Scrolls. We have heard a lot about those in our time because they were discovered not too long ago. They basically reflect the thought and practices of various separatist groups that pulled away from Rome and away from the common culture of the day, trying to preserve the values and certain things that they considered to be important.
Fourthly, the Septuagint, often abbreviated LXX. There is a belief that seventy scholars produced this Bible in seventy days, which probably is not true, but it is a nice story. The Septuagint is the Greek translation of the Hebrew scriptures. Now remember that Greece made their language the main language, and that language now is a key in carrying the scriptures through the land. The Septuagint becomes a key tool, the translation from Hebrew to Greek; and as people learn the Greek language through the land, then that addition of the Hebrew scriptures becomes the much quoted, much read edition through the Roman Empire.
Religions
In this period of time the Jewish religion takes a significant shift. Temple worship is re-established, but it struggles. The priests become more and more politically connected to whoever the ruler is and they become a little more compromising in their approach. In response the synagogue appears. The synagogue is a local-level gathering that teaches the people and is heavily moral and ethical. The synagogue is very formal and has a great influence on the people.
It is the Temple-synagogue separation which leads to the rise of two groups which we see clearly in the New Testament writings – the Pharisees and Sadducees. The Sadducees are connected to the Temple. The High Priest comes from this group, as do most of the priests. They become very connected to the rulers of the land, to the Greeks, and when independence comes they are very prominent; and when Rome comes on the scene, they connect themselves to Rome. Power, wealth and prestige are attached to being a Temple servant. The Pharisees are connected to the synagogue and they become the local teachers. They ask much more of the people, brilliant by all accounts in their formalism and moralism.
Another group arises called the Sanhedrin. They are a ruling counsel of Jews that have managed to stay in power from the time of the Greeks and they basically are the local group, the Judean group, that brings civil law to the people. They answer to the rulers, but they are the Jewish people who rule during this time.
There is another group that does not connect to the politics of the time, and they are known as the scribes. The scribes are teachers and they are those who were most involved in the preservation of the Hebrew scriptures.
There are Herodians who are Jewish people, who have been connected very closely to the Roman rulers. They tend to be wealthy people who attached their wealth to Rome, known as the Herodians because the Herods were the rulers from Rome who ruled over this area we know as Judea. And as opposed to those, we have a group called the Essenes. They are a large, fairly diverse group that pulled out of civilisation, becoming separatists. Many of them moved down by the Dead Sea and wrote the Dead Sea Scrolls.
The stage is set for Jesus to arrive on the scene. The time is ready for God to send his only son into the world, the promised Messiah who will fulfill God’s plan for the people he made all those years and pages ago in Genesis 2.






